ECONOMICS STRATEGY
ECONOMICS
(Economic and Social Development-Sustainable, Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector Initiatives, etc.)
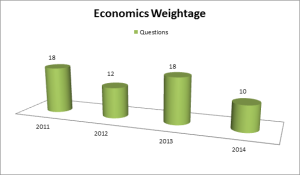
1. Weightage given since 2011
2. How to Prepare
3. Basic Economic and Indian Economy
2. How to Prepare
3. Basic Economic and Indian Economy
Economy may be daunting to some, but the questions are based on your conceptual understanding of macroeconomics. No matter how many times you read and mug-up the data, you are bound to falter in the exam. Conceptual clarity is what matters the most in Economics.
Weightage given to Economics (since 2011)
If your basic funda’s of Economics is sound, then you will even be able to get all answers right in Prelims . So our sincere advice to you is to invest more time in understanding the concepts and analyzing how one concept is linked to another.
For Example:
| If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (2014)(a) decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
(b) increase the tax collection of the Government
(c) increase the investment expenditure in the economy
(d) increase the total savings in the economy
Solution (c)
|
| Under which of the following circumstances may ‘capital gains’ arise? (2012)
1. When there is an increase in the sales of a product2. When there is a. natural increase in the value of the property owned
3. When you purchase a painting and there is a growth in its value due to increase in its popularity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (b)
|
How to Study Economics?
Some of them have misconceptions that Economics is only about ‘money’. No its about choices. Choices or decisions made based on the resource available (time, capability, money, interest etc.)
Decisions made in midst of alternatives at the National level is known as ‘Macroeconomics’ (Government making a decision to blend 10% Ethanol in petrol) and if the same choices/decisions are made at the individual level, it is known as ‘Micro-economics’.
Economics has so much of relevance to our day-to-day lives. Be it the choice that you make to take-up this exam or even choose or website ‘IASbaba’ for your preparation. It’s all about making choices suiting to your needs and available resources.
This makes reading Economics enjoyable and meaningful !!
Once you get hold of this subject, it will take very less time to revise and also more accuracy can be achieved in the exam.
Basic Economic and Indian Economy:
- Introduction to Economics:
Focus:
Understanding the basic concepts of:
- MacroEconomics – Poverty, Growth, Employment etc
- Microeconomics – decisions/choices made at a company, household or an individual level
- Difference between Growth and Development; indicators used to measure.
- Example: To measure Growth- GDP is used and for Development – HDI (Human Development Index)
- National Income Accounting – Gross National Product (GNP), Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Income (GNI), Factor cost, Market Price, Purchasing power parity(PPP), Per-Capita Income (PCI) – a general understanding on how they are calculated and what all factors go into their calculation
- Example: GDP is calculated using either of the following 3 methods- production method, expenditure method, income method.
- Primary , Secondary, Tertiary Sectors – what constitutes each sector? What are their contributions to the GDP
- Example: Primary sector covers agriculture and allied activities, mining . It contributes 13.7% to India’s GDP
- Capitalist, State, Mixed Economic System – which type of Economic system India has adopted and why?
Note: Don’t just read definitions, analyze! For example: When do we use GDP for measurement of Growth and not GNP? Which method is followed in India and why?
When we say ‘why’ a particular method was adopted- it means that, one has to understand both positives and negatives of the method.
Example: 2013 Previous Year Question
The national income of a country for a given period is equal to the:(a) total value of goods and services produced by the nationals(b) sum of total consumption and investment expenditure(c) sum of personal income of all individuals
(d) money value of final goods and services produced
Solution (a)
|
2011 Previous Year Question
| A “closed economy” is an economy in which(a.) the money supply is fully controlled
(b.) deficit financing takes place
(c.) only exports take place
(d.) neither exports nor imports take place
Solution (d)
|
- Growth & Development
Focus:
- Poverty– concepts like Below Poverty line (BPL), Poverty Gap, Poverty estimates by National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO), which Institution in India decides on Poverty line- Planning Commission
- Different Committees set-up to measure poverty, methodology used – Alag committee, Lakadwala, Suresh Tendulkar Committee, NC Saxena Committee, Rangarajan Committee – A general understanding of how each committee differed in their measurement.
- Example: Rangarajan Committee was set-up by Planning Commission in 2012; Methodology used is ‘Monthly Expenditure of family of five’. According to the estimates- poverty per day per person in urban area is 47 Rs and in rural area it is 32 Rs
- Inequality– how is it measured –Gini co-efficient , Lorenz Curve; concepts like relative inequality, absolute inequality.
- Issues with employment, different types of unemployment like disguised unemployment, underemployment etc; Globalization and its impact on labour.
- Demographic Dividend, Skill Development
- Development Indicators from International organisations like HDI, MPI (Multiple Poverty Index), Millennium Development Goals etc.
Note: Make a note of the Government Schemes, Committees related to growth, development, eradication of Poverty, Employment, Labour issues etc. like MGNREGA, National Rural Livelihood Mission, Bharat Nirman etc.
Initiatives like ‘Make in India’, Innovation Council, Skill Development Initiative Scheme (SDIS)
Example: 2013 Previous Year Question
| Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Solution (c)
|
| Economic growth in country X will necessarily have to occur if(2013)(a) there is technical progress in the world economy
(b) there is population growth in X
(c) there is capital formation in X
(d) the volume of trade grows in the world economy
Solution (c)
|
- Inflation and Business Cycle
Focus:
- Inflation, Depression, Recession and related terms and concepts like deflation, disinflation, reflation, stagflation, Philip’s curve
- Types of Inflation – based on the rate of growth of the prices– creeping, trotting, galloping, hyper-inflation
- Types of Inflation – based on the causes– Demand-pull, Cost-push, Structural, Speculation.
- Impact of Inflation on Indian Economy, different stakeholders in the economy. Is a minimum inflation necessary? If so why?
- Inflation measurements like CPI, WPI, GDP deflator
- Composition or what constitutes these indicators
- Their merits and demerits
- Which measurement is better indicator of inflation and why? Which index is used to measure inflation in India currently?
- Base year from which it’s calculated.
- What is this Base year?
- Why does Government change the Base Year?
- What impact it has on the economic growth or inflation?
- Example: In WPI there are totally 676 items, out of that 20% weightage is given to Food, 14% to Power and Fuel, 66% to Manufactured goods. It does not include Services. Base year for WPI is 2010-11. It is published by Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Role of Government and RBI in controlling inflation
Example: 2013 Prelims Question
| Consider the following statements : (2013)1. Inflation benefits the debtors. 2. Inflation benefits the bond-holders.Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2Solution (a) |
| A rise in general level of prices may be caused by: (2013)1. an increase in the money supply 2. a decrease in the aggregate level of output 3. an increase in the effective demandSelect the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3Solution (d) |
2011 Prelims Question
| A rapid increase in the rate of inflation is sometimes attributed to the “base effect”. What is “base effect”?(a.) It is the impact of drastic deficiency in supply due to failure of crops (b.) It is the impact of the surge in demand due to rapid economic growth (c.) It is the impact of the price levels of previous year on the calculation of inflation rate (d.) None of the statements (a), (b) and (c) ‘given above is correct in this contextSolution (c) |
- Money and Banking Systems
Focus:
- Role and functions of RBI
- Monetary Policy/measures taken by RBI like Bank rate, repo rate, reverse repo rate, Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Cash reserve Ratio (CRR), Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF)
- Why are these measures taken?
- What impact it has on the Supply of money, Inflation and the Economy?
- Different types of Banks and their functioning– Commercial Banks, RRB’s, Development banks, NABARD, Co-operative Banks, Development Banks, Merchant Banks, Non-Banking Financial Company’s (NBFC’s), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) etc.
- Functions of these Banks, to whom do they lend?
- How are these Banks regulated? Concepts like priority sector lending
- Example: NBFC’s are regulated by RBI, unlike the normal banks, NBFC cannot accept demand deposits (DD); NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue ‘cheques’ drawn on itself.
- Banking reforms like Bank Nationalisation (1969, 1980) Basel Norms etc.
- Why were/are these reforms needed?
- What was/is the Purpose of these reforms
- Understand Key-Terms– Financial Inclusion, Fiscal Consolidation, Narrow Banking, Non-Performing Assets, Shadow Banks, Weak Bank, Core Banking, Bank Run, Priority Sector lending, Capital to Risk Weighted Assets (CRAR) etc., and other related concepts related to Banking – what steps have been taken by the Government and RBI in this regard.
- Steps taken by government with regard to Financial Inclusion.
- Example: Introduction of Business Correspondent model in rural areas or Woman only banks, Jan Dan Yojana, Micro-finance, Mudra Bank etc
- Recent Committee’s setup with regard to Banking Reforms and its important recommendations
Few Example’s from Previous Year’s Prelims Questions Paper
| If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (2014)A. decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy B. increase the tax collection of the Government C. increase the investment expenditure in the economy D. increase the total savings in the economySolution (c) |
| The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of (2013)1. liquidity of assets 2. branch expansion 3. merger of banks 4. winding-up of banksSelect the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1 and 4 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 only (c) 1, 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4Solution (d) |
| What is/are the facility/facilities the beneficiaries can get from the services of Business Correspondent (Bank Saathi) in branchless areas? (2014)1. It enables the beneficiaries to draw their subsidies and social security benefits in their villages. 2. It enables the beneficiaries in the rural areas to make deposits and withdrawals.Select the correct answer using the code given below.A.1 only B.2 only C.Both 1 and 2 D.Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (c)
|
Continue to Read ->
ECONOMICS STRATEGY-2
5. Fiscal Policy:
A. Fiscal Measures
Focus:
- Fiscal policy, Finance Commission (14th FC and its important provisions)
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budgetary Management(FRBM) Act, other actions taken by the Finance Ministry (Government), Disinvestment of Public Sector Units (PSU’s) to improve the financial health of the Economy
- What is Financial Stability? Steps taken by Government in this regard
- Financial Sector Reforms brought about by the government in these sectors -Banking, Insurance, Provident Fund (PF).
Example: In 2015, Raising of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) limit in defence to 49%, In Railway infrastructure to 100% etc.
- Financial Regulators – Reserve Bank of India(RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India(SEBI), Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA), Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) – powers, functions, jurisdiction issues between the regulators
- Financial Stability and Development Council – objective and functions
- Economic Reforms– concepts related to privatization and globalization, SEZ’s etc.
- Sources of financial resources for Government – Tax and Non-tax revenue (Foreign aid, Disinvestment from PSU’s etc), Disinvestment, Borrowings (internal and external), User Charges.
B. Budget
Focus:
- Components of Budget, Revenue and Capital receipts and expenditure
- What constitutes Plan and Non plan expenditure? Difference between them.
- Key Terms like pubic debt, External debt, Internal debt, Revenue Deficit, Primary Deficit, deficit financing, fiscal consolidation Zero-based Budgeting
- Steps taken by the government to bring down the Fiscal Deficit
Example: FRBM Act
Example (2014 Prelims Questions Paper):
| With reference to Union Budget, which of the following, is/are covered under Non-Plan Expenditure?
1. Defense expenditure
2. Interest payments 3. Salaries and pensions 4. Subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2, 3 and 4
D. None
Solution (c )
|
Example (2013 Prelims Questions Paper):
| In India, deficit financing is used for raising resources for
(a) economic development
(b) redemption of public debt (c) adjusting the balance of payments (d) reducing the foreign debt
Solution (a)
|
C. Taxation
Focus:
- Direct, Indirect tax and other Taxes like Pigovian tax, Ad Valorem tax, Tobin Tax, Difference between a Cess and a Surcharge
- Direct Tax like Corporate Tax, Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Stock Market transactions
- Indirect Tax like Excise Tax, Customs, VAT, Service tax
- Taxation Reforms – Direct Tax Code(DTC), General Anti-Avoidance Rule(GAAR), Goods and Service Tax (GST).
Example: With regard to GST – Purpose; advantages and disadvatages of GST; issues with regard to implementation of GST;
- Understand the basic concepts like what is Tax Base, Progressive taxation,Tax Expenditure, Tax avoidance, Tax evasion, Tax Havens, Tax elasticity, Tax Buoyancy, Laffer curve, Crowding-out.
Example (2014 Prelims Questions Paper):
| The sales tax you pay while purchasing a toothpaste is a
a. tax imposed by the Central Government.
b. tax imposed by the Central Government but collected by the State Government c. tax imposed by the State Government but collected by the Central Government d. tax imposed and collected by the State Government
Solution (d)
|
2011 Prelims Questions Paper:
| Which one of the following is not a feature of “Value Added Tax”?
(a.) It is a multi-point destination-based system of taxation
(b.) It is a tax levied on value addition at each stage of transaction in the production-distribution chain (c.) It is a tax on the final consumption of goods or services and must ultimately be borne by the consumer (d.) It is basically a subject of the Central Government and the State Governments are only a facilitator for its successful implementation
Solution (c)
|
D. Planning
Focus:
- Institutions involved in Planning in India
- A general idea on how planning has evolved over the years (since Independence)
- How planning takes place at the State and National level
- New institution – Niti Ayog
- Its purpose
- Why was Planning Commission dissolved?
- Issues between Planning Commission and Finance Commission
Note: Make a note on the latest committees set-up with regard to Fiscal and Economic Reforms like Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission (FSLRC), Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC), Nachiket mor committee etc.
Example (2014 Prelims Questions Paper):
| The main objective of the 12th Five-Year Plan is
A. inclusive growth and poverty reductions
B. inclusive and sustainable growth C. sustainable and inclusive growth to reduce unemployment D. Faster, sustainable and more inclusive growth.
Solution (d)
|
6. Market:
Focus:
- Money Market – Treasury Bills, Commercial paper, Certificate of Deposit, Call Money
- Capital Market – Government Securities (G-Secs)
- Difference between Money and Capital market
- A general idea about Stock-exchanges in India – BSE, NSE; Nifty (Abroad); What is SENSEX- what does it indicate?
- Regulatory Bodies – SEBI, IRDA , PFRDA – their power, functions in regulating Market, Mutual funds, Pension Fund etc.; reforms brought about by the Regulatory Bodies
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI’s) and Foreign Institutional Investors (FII’s)
- On what basis are they classified as FDIs and FIIs?
- Differences between them
- Why are FII’s called ‘hot money’ or ‘Portfolio investment?
- Which type of investment would be better for India?
- Other investments such as Qualified Institutional Placement (QIPs) – Angel investors, Venture Capitals, Foreign institutional investors, Mutual Funds, Public Financial institutions
- Have a Basic understanding of these terms– Primary market, Secondary market, Bull and Bear (what does it symbolize), Derivatives, Futures, Bonds, Debentures – partially and fully convertible , Participatory Notes, Hedge Funds, Blue chip shares, Market depth.
- Mechanisms to raise money in the Capital Market in India by Foreign countries- Indian Depository Receipts (IDR’s); Similarly for an Indian company to raise money in the Foreign market –Global Depository Receipts (GDR’s) and in America it is known as American Depository Receipts (ADR’s)
Example (2014 Prelims Question)
| What does venture capital mean?
A. A short-term capital provided to industries
B. A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs C. Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses D. Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Solution (b)
|
2012 Prelims Question Paper
| Which of the following would include Foreign Direct Investment in India?
1. Subsidiaries of companies in India
2. Majority foreign equity holding in Indian companies 3. Companies exclusively financed by foreign companies 4. Portfolio investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 4 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 only
Solution (d)
|
7. Public Sector Public Sector Units (PSU’s)
Focus:
- Organisational Structure of PSU’s – Departmental Undertakings, Statutory Corporations, Control Boards, Co-operative Societies, Companies registered under the Companies Act 1956
- Purpose/Objectives of PSU’s
- Reforms – post Liberalisation, Privatization, Globalisation (LPG) era- Disinvestment, Memorandum of Understanding (MOUs), Miniratnas, Navaratna, Maharatna, New Companies Act, 2013, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- What is Corporate Governance? What are its Objectives?
- Industry:
- A general idea about Industrial Policies in India
- Medium and Small-Scale Enterprises (MSME’s ), Small-Scale Industries (SSI), Village and Cottage Industries (VCI)- On what basis are they classified so
- What measures are taken by Government to revive these industries?
Example: (2011 Prelims Question)
|
Why is the Government of India disinvesting its equity in the Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)?
1. The Government intends to use the revenue earned-from the disinvestment mainly to pay back the external debt.
2. The Government no longer intends to retain the management control of the CPSEs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) I only
(b.) 2 only (c.) Both 1 and 2 (d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (d)
|
ECONOMICS STRATEGY-3
8. External Sector/Foreign Trade
Focus:
- India’s Foreign Policy – recent initiatives taken
- Balance of Payment (BoP)
- What constitutes BoP?
- What do you understand by ‘Invisibles’? How does it affect BoP?
- External Commercial Borrowings (ECB)
- What does it constitute, what is it meant for?
- Who regulates it?
- Who borrows from it? Example: Corporate sector , Government
- Capital and Current Account Convertibility– India has full Current Account Convertibility but when it comes to Capital Account Convertibility, it is only partial. Why?
- A general idea about MRTP Act, 1969; FERA, 1973; FEMA, 1999 – this will help you in understanding the changes made to capital account convertibilityand why India is yet to go for full convertibility and what is the present status
- Current Account Deficit (CAD)
- What is CAD?
- Who reports CAD?
- Why India has huge CAD? Is a minimum CAD necessary? What are the measures taken by India to reduce CAD?
- Rupee appreciation, depreciation
- How is Rupee value determined?
- How and why does Rupee appreciate or depreciate?
- Its impact on domestic and external market? On imports and exports.
- What measures does RBI take when rupee appreciates or depreciates? How does it impact Forex Reserves?
- Difference between Depreciation and Devaluation of currency (in Indian – rupee) Why does a country devaluate its currency?
- Currency Exchange rate
- How is the currency exchange rate determined?
- Who determines it ?
- Exchange rate interms of Purchasing power parity (PPP).
- What is Nominal Effective Exchange Rate(NEER), Real Effective Exchange Rate(REER)?
- Forex Reserves
- What does it constitute?
- What is the use of having Forex Reserve?
- Why do we need more Forex Reserves?
- How can we accumulate more Forex reserves?
- Concepts like Trade deficits, Elasticity of Demand, Savings, Investment, J-curve effect
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA)
- Differences between the two agreements
- How is it different from Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
- Benefits that Indian will have with these agreements
- A general awareness on the countries with which India has signed these agreements recently and what are the issues involved and benefits from the same
Note: Issues like GAAR, Euro Zone Crisis, Gold imports or any issue that you come across in the newspaper, make a note of it.
Example: (2014 Prelims Questions Paper):
| With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account?1. Balance of trade 2. Foreign assets 3. Balance of invisibles 4. Special Drawing RightSelect the correct answer using the code given below.A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3
C. 1 and 3
D. 1, 2 and 4
Solution (c)
| |
| (2013 Prelims Questions Paper):
Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves?
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs (c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs (d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Solution (b)
| |
| Which of the following constitute Capital Account? (2013)
1. Foreign Loans
2. Foreign Direct Investment 3. Private Remittances 4. Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Solution (b)
|
| (2012 Prelims Questions Paper):
Consider the following statements:The price of any currency in international market is decided by the
1. World Bank 2. demand for goods/services provided by the country concerned 3. stability of the government of the concerned country 4. economic potential of the country in question
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Solution (b)
|
9. International Economic Organisations
Focus:
- Bretton Wood Twins- World Bank, IMF
- A general awareness on- When was it started? Where is its Headquarters?
- What is the purpose? To whom do they lend money to?
- How does It function?
- Reports published by WB and IMF
- Recently joined members of WB and IMF
- World bank and World bank Groups
- Relevance of IMF and WB to the developing countries (especially India)
Example: IMF was setup in 1944, its HQ- Washington, USA. Purpose- to facilitate balanced growth of International trade, Exchange rate, to overcome Balance of Payment crisis and it lends only to member countries and not for a specific purpose, unlike WB. Functioning- Each member is assigned a quota (based on size of the economy), which indicates the voting power, access to financing, the amount a member is obliged to provide to the IMF
- What are SDR’s? how does it help member countries?
- World Trade Organisation (WTO)
- A general idea on how WTO came into being and what was the set-up before WTO
- Difference between General Agreement on tariffs and Trade (GATT) and WTO
- What is the objective of WTO? How does it function (example- WTO works on the principle ‘one country one vote’, unlike WB or IMF)
- Recently joined members of WTO
- Doha round – why is Doha round stalled? Issue’s between developed and developing countries
- WTO and India – how has it helped India, if so in what way? what are the issues- is it a boon or a bane to India?
- WTO principles– Most Favoured Nation (MFN)- non-discriminatory Trade, General system of Preference (GSP) for developing countries and Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA), Free Trade Agreement (FTA) for economics integration
- Stages in economic integration – PTA > FTA > Customs Union > Monetary Union
- Others Safeguard mechanisms– Safeguard Mechanisms, Sanitary and Phytosanitary agreement (SPS), Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- WTO agreements
- Agreement on Agriculture(AoA) – Domestic support (Green Box, Amber Box, Blue Box), Export subsidies, Market access
- Agreement on TRIPS and Patent Issues
- Make a note of the current issues related to Patent;
- Copyrights, Trademark, Industrial Design right – for what type of products are each given
Example: Copyrights for creative and artistic work, whereas Patents for inventions
- TRIPS agreement and Safeguards – Parallel importation, Compulsory Licensing
- Geographical indicators – significance; to what products and for whom are they granted to? A general awareness on the latest products which have been granted the status
- General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Difference between Protectionism and Import Substitution
- instruments of protectionism- tariffs, import quotas, administrative barriers, anti-dumping duties, direct or export subsidies, exchange rate manipulation
- A general idea about Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) by World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO), Non-Agricultural Market Access (NAMA) group, NAMA 11
- Regional trade agreements and Regional Groupings like ASEAN FTA, SAFTA, MERCOSUR, BRICS, SAARC, The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), G20 etc.
- their objectives
- recent summits especially where India is a major player in the grouping
- recent initiatives undertaken in the summits
- how do these initiatives help India?
Example: BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) latest summit (2014) was held in Brazil. Here, they came up with an initiative to create US$100 billion New Development Bank (NDB). NDB is seen as an alternative to the existing US-dominated World Bank and IMF. The bank is set up to foster greater financial and development cooperation among the five emerging markets. Unlike the World Bank, which assigns votes based on capital share, in the New Development Bank each participant country will be assigned one vote, and none of the countries will have veto power.
Note: Make a note of the International Economic organisations to which India is not a member of; and on Asian Development Bank (ADB), G4.
| Example (2014 Prelims Questions Paper): Which of the following organizations brings out the publication known as ‘World Economic Outlook’?A. The International Monetary FundB. The United Nations Development Programme
C. The World Economic Forum
D. The World Bank
Solution (a)
|
10. Economic Survey
Focus:
Make note of the Key terms and their meaning, especially the new ones. Since UPSC has the knack of picking up specific terms from the Economic Survey in both Prelims and Mains Exam.
| 2012 Prelims Question
In India, in the overall Index of Industrial Production, the Indices of Eight Core Industries have a combined weight of 37-90%. Which of the following are among those Eight Core Industries?
1. Cement
2. Fertilizers
3. Natural gas
4. Refinery products
5. Textiles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Solution (c)
|
Note : Economic Terms– Inflation, Recession, Depression, Balance of Payment, Financial Inclusion, Fiscal Consolidation, Deficit Financing, Overheated Economy, Fiscal drag, Fiscal Neutrality, Giffen goods etc. – Basic understanding of the key terms is important.
11. Social Development, Poverty and Inclusion:
This is a dynamic area as questions will be mostly related to recent developments and programs and policies of the government to address issues related to poverty, inclusion, growth and development. It has a wider perspective and also is linked with the current events.
Example: Malnutrition- reasons associated with it, Poverty Indexes like Multi-poverty Index, committees set up like Rangarajan committee’s estimate of Poverty, BPL, APL, Income gap, Jan Dan Yojna etc.
12. Demographics:
This section overlaps with Human geography. Statistical data from Economic Survey will be helpful here like population, working age of the population, sex-ratio, literacy, Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR), Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) etc
- What are the issues (Ex: low literacy ),
- Measures taken by the government in this regard.
13. Social Sector initiatives:
This part is already covered under Public Policy & Right’s issue under ‘Polity’.
Previous Years Questions from ‘Economics‘ <-Click Here
Basic Economic and Indian Economy: Social Development, Poverty and Inclusion: Prelims Questions and Solutions
India has experienced persistent and high food inflation in the recent past. What could be the reasons?(2011)
- Due to a gradual switchover to the cultivation of commercial crops, the area under the cultivation of food grains has steadily decreased in the last five years by about 30%.
- As a consequence of increasing incomes, the consumption patterns of the% people have undergone a significant change.
- The food supply chain has structural constraints.
Which of the statements given above1 are correct?
(a.) 1 and 2 only
(b.) 2 and 3 only
(c.) 1 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (b)
In terms of economy, the visit by foreign nationals to witness the XIX Common Wealth Games in India amounted to(2011)
(a.) Export
(b.) Import
(c.) Production
(d.)Consumption
Solution (a)
Which one of the following statements appropriately describes the “fiscal stimulus”?(2011)
(a.) It is a massive investment by the Government in manufacturing sector to ensure the supply of goods to meet the demand surge caused by rapid economic growth
(b.) It is an intense affirmative action of the Government to boost economic activity in the country
(c.) It is Government’s intensive action on financial institutions to ensure disbursement of loans to agriculture and allied sectors to promote greater food production and contain food inflation
(d.) It is an extreme affirmative action by the Government to pursue its policy of financial inclusion
Solution (b)
Consider the following actions which the Government can take:
- Devaluing the domestic currency.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs.
Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit?
(a.) 1 and 2
(b.) 2 and 3
(c.) 3 only
(d.) 1 and 3
Solution (a)
A rapid increase in the rate of inflation is sometimes attributed to the “base effect”. What is “base effect”?(2011)
(a.) It is the impact of drastic deficiency in supply due to failure of crops
(b.) It is the impact of the surge in demand due to rapid economic growth
(c.) It is the impact of the price levels of previous year on the calculation of inflation rate
(d.)None of the statements (a), (b) and (c) ‘given above is correct in this context
Solution (c)
Why is the offering of “teaser loans” by commercial banks a cause of economic concern?(2011)
- The teaser loans are considered to be an aspect of sub-prime lending and banks may be exposed to the risk of defaulters in future.
- In India, the teaser loans are mostly given to inexperienced entrepreneurs to set up manufacturing or export units.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (c)
In the context of Indian economy, consider the following statements :(2011)
- The growth rate of GDP has steadily increased in the last five years.
- The growth rate in per capita income has steadily increased in the last five years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (b)
In India, which of the following have the highest share in the disbursement of credit to agriculture and allied activities?(2011)
(a.) Commercial Banks
(b.) Cooperative Banks
(c.) Regional Rural Banks
(d.) Microfinance Institutions
Solution (a)
Economic growth is usually coupled with (2011)
(a.) Deflation
(b.) Inflation
(c.) Stagflation
(d.) Hyperinflation
Solution (b)
The lowering of Bank Rate by the Reserve Bank of India leads to (2011)
(a.) More liquidity in the market
(b.) Less liquidity in the market
(c.) No change in the liquidity in the market
(d.) Mobilization of more deposits by commercial banks
Solution (a)
Which one of the following is not a feature of “Value Added Tax”? (2011)
(a.) It is a multi-point destination-based system of taxation
(b.) It is a tax levied on value addition at each stage of transaction in the production-distribution chain
(c.) It is a tax on the final consumption of goods or services and must ultimately be borne by the consumer
(d.) It is basically a subject of the Central Government and the State Governments are only a facilitator for its successful implementation
Solution (c)
A “closed economy” is an economy in which (2011)
(a.) the money supply is fully controlled
(b.) deficit financing takes place
(c.) only exports take place
(d.) neither exports nor imports take place
Solution (d)
Both Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) are related to investment in a country. Which one of the following statements best represents an important difference between the two? (2011)
(a.) FII helps bring better management skills and technology, while FDI only brings in capital
(b.) FII helps in increasing capital availability in general, while FDI only targets specific sectors
(c.) FDI flows only into the secondary market, while FII targets primary market
(d.) FII is considered to be more stable than FDI
Solution (b)
Microfinance is the provision of financial services to people of low-income groups. This includes both the consumers and the self-employed. The service/services rendered under micro-finance is/are: (2011)
- Credit facilities
- Savings facilities
- Insurance facilities
- Fund Transfer facilities
Select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 1 and 4 only
(c.) 2 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (d)
Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 1 and 2 only
(c.) 2 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Why is the Government of India disinvesting its equity in the Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)? (2011)
- The Government intends to use the revenue earned-from the disinvestment mainly to pay back the external debt.
- The Government no longer intends to retain the management control of the CPSEs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) I only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (d)
2012 UPSC Prelims Questions and Solutions
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a bankers’ bank. This would imply which of the following? (2012)
- Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
- The RBI lends funds to the commercial banks in times of need.
- The RBI advises the commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Under which of the following circumstances may ‘capital gains’ arise? (2012)
- When there is an increase in the sales of a product
- When there is a. natural increase in the value of the property owned
- When you purchase a painting and there is a growth in its value due to increase in its popularity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (b)
Which of the following measures would result in an increase in the money supply in the economy? (2012)
- Purchase of government securities from the public by the Central Bank
- Deposit of currency in commercial banks by the public
- Borrowing by the government from the Central Bank
- Sale of government securities to the public by the Central Bank
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Solution (c)
Which of the following would include Foreign Direct Investment in India? (2012)
- Subsidiaries of companies in India
- Majority foreign equity holding in Indian companies
- Companies exclusively financed by foreign companies
- Portfolio investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 only
Solution (d)
Consider the following statements: (2012)
The price of any currency in international market is decided by the
- World Bank
- demand for goods/services provided by the country concerned
- stability of the government of the concerned country
- economic potential of the country in question
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Solution (b)
The basic aim of Lead Bank Scheme is that: (2012)
(a) big banks should try to open offices in each district
(b) there should be stiff competition among the various nationalized banks
(c) individual banks should adopt particular districts for intensive development
(d) all the banks should make intensive efforts to mobilize deposits
Solution (c)
In India, in the overall Index of Industrial Production, the Indices of Eight Core Industries have a combined weight of 37-90%. Which of the following are among those Eight Core Industries? (2012)
- Cement
- Fertilizers
- Natural gas
- Refinery products
- Textiles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Solution (c)
The balance of payments of a country is a systematic record of (2012)
(a) all import and transactions of a during a given period normally a year
(b) goods exported from a country during a year
(c) economic transaction between the government of one country to another
(d) capital movements from one country to another
Solution (a)
The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of (2013)
- liquidity of assets
- branch expansion
- merger of banks
- winding-up of banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (d)
An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the: (2013)
(a) market rate of interest is likely to fall
(b) Central Bank is no longer making loans to commercial banks
(c) Central Bank is following an easy money policy
(d) Central Bank is following a tight money policy
Solution (d)
In India, deficit financing is used for raising resources for (2013)
(a) economic development
(b) redemption of public debt
(c) adjusting the balance of payments
(d) reducing the foreign debt
Solution (a)
Which of the following constitute Capital Account? (2013)
- Foreign Loans
- Foreign Direct Investment
- Private Remittances
- Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Solution (b)
Consider the following statements : (2013)
- Inflation benefits the debtors.
- Inflation benefits the bond-holders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (a)
Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Solution (c)
Consider the following liquid assets: (2013)
1.Demand deposits with the banks
2.Time deposits with the banks
3.Savings deposits with the banks
4.Currency
The correct sequence of these decreasing order of Liquidity is
(a) 1-4-3-2
(b) 4-3-2-1
(c) 2-3-1-4
(d) 4-1-3-2
Solution (d)
In the context of Indian economy,Open Market Operations’ refers to: (2013)
(a) borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
(b) lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
(c) purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
(d) None of the above
Solution (c)
Priority Sector Lending by banks in India constitutes the lending to: (2013)
(a) agriculture
(b) micro and small enterprises
(c) weaker sections
(d) All of the above
Solution (d)
A rise in general level of prices may be caused by: (2013)
- an increase in the money supply
- a decrease in the aggregate level of output
- an increase in the effective demand
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves? (2013)
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
(c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
(d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Solution (b)
Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary in its effect? (2013)
(a) Repayment of public debt
(b) Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
(c) Borrowing from banks to finance a budget deficit
(d) Creating new money to finance a budget deficit
Solution (d)
Supply of money remaining the same when there is an increase in demand for money, there will be: (2013)
(a) a fall in the level of prices
(b) an increase in the rate of interest
(c) a decrease in the rate of interest
(d) an increase in the level of income and employment
Solution (b)
Economic growth in country X will necessarily have to occur if (2013)
(a) there is technical progress in the world economy
(b) there is population growth in X
(c) there is capital formation in X
(d) the volume of trade grows in the world economy
Solution (c)
The national income of a country for a given period is equal to the: (2013)
(a) total value of goods and services produced by the nationals
(b) sum of total consumption and investment expenditure
(c) sum of personal income of all individuals
(d) money value of final goods and services produced
Solution (a)
Which of the following grants/ grant direct credit assistance to rural households? (2013)
- Regional Rural Banks
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
- Land Development Banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (c)
The terms ‘Marginal Standing Facility Rate’ and ‘Net Demand and Time Liabilities’, sometimes appearing in news, are used in relation to (2014)
- banking operations
- communication networking
- military strategies
- supply and demand of agricultural products
Solution (a)
What is/are the facility/facilities the beneficiaries can get from the services of Business Correspondent (Bank Saathi) in branchless areas?(2014)
- It enables the beneficiaries to draw their subsidies and social security benefits in their villages.
- It enables the beneficiaries in the rural areas to make deposits and withdrawals.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (c)
If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (2014)
- decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
- increase the tax collection of the Government
- increase the investment expenditure in the economy
- increase the total savings in the economy
Solution (3)
In the context of Indian economy which of the following is/are the purpose/purposes of ‘Statutory Reserve Requirements’?
- To enable the Central Bank to control the amount of advances the banks can create
- To make the people’s deposits with banks safe and liquid
- To prevent the commercial banks from making excessive profits
- To force the banks to have sufficient vault cash to meet their day-to-day requirements
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (b)
If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will
- decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
- increase the tax collection of the Government
- increase the investment expenditure in the economy
- increase the total savings in the economy
Solution (c)
With reference to Union Budget, which of the following is/are covered under Non-Plan Expenditure?
- Defense -expenditure
- Interest payments
- Salaries and pensions
- Subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- None
Solution (c)
The sales tax you pay while purchasing a toothpaste is a
- tax imposed by the Central Government.
- tax imposed by the Central Government but collected by the State Government
- tax imposed by the State Government but collected by the Central Government
- tax imposed and collected by the State Government
Solution (d)
The main objective of the 12th Five-Year Plan is
- inclusive growth and poverty reductions
- inclusive and sustainable growth
- sustainable and inclusive growth to reduce unemployment
- Faster, sustainable and more inclusive growth.
Solution (d)
What does venture capital mean?
- A short-term capital provided to industries
- A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
- Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
- Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Solution (b)
With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account?
- Balance of trade
- Foreign assets
- Balance of invisibles
- Special Drawing Right
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 4
Solution (c)
Which of the following organizations brings out the publication known as ‘World Economic Outlook’?
- The International Monetary Fund
- The United Nations Development Programme
- The World Economic Forum
- The World Bank
Solution (a)
Demographics:
India is regarded as a country with “Demographic Dividend”. This is due to: (2011)
(a.) Its high population in the age group below 15 years
(b.) Its high population in the age group of 15-64 years
(c.) Its high population in the age group above 65 years
(d.) Its high total population
Solution (b)
Consider the following specific stages of demographic transition associated with economic development : (2012)
- Low birthrate with low death rate
- High birthrate with high death rate
- High birthrate with low death rate
Select the correct order of the above stages using the codes given below :
(a) 1, 2, 3
(b) 2, 1, 3
(c) 2, 3, 1
(d) 3, 2, 1
Solution (c)
To obtain full benefits of demographic dividend, what should India do? (2013)
(a) Promoting skill development
(b) Introducing more social security schemes
(c) Reducing infant mortality rate
(d) Privatization of higher education
SolutiBasic Economic and Indian Economy: Social Development, Poverty and Inclusion: Prelims Questions and Solutions
India has experienced persistent and high food inflation in the recent past. What could be the reasons?(2011)
- Due to a gradual switchover to the cultivation of commercial crops, the area under the cultivation of food grains has steadily decreased in the last five years by about 30%.
- As a consequence of increasing incomes, the consumption patterns of the% people have undergone a significant change.
- The food supply chain has structural constraints.
Which of the statements given above1 are correct?
(a.) 1 and 2 only
(b.) 2 and 3 only
(c.) 1 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (b)
In terms of economy, the visit by foreign nationals to witness the XIX Common Wealth Games in India amounted to(2011)
(a.) Export
(b.) Import
(c.) Production
(d.)Consumption
Solution (a)
Which one of the following statements appropriately describes the “fiscal stimulus”?(2011)
(a.) It is a massive investment by the Government in manufacturing sector to ensure the supply of goods to meet the demand surge caused by rapid economic growth
(b.) It is an intense affirmative action of the Government to boost economic activity in the country
(c.) It is Government’s intensive action on financial institutions to ensure disbursement of loans to agriculture and allied sectors to promote greater food production and contain food inflation
(d.) It is an extreme affirmative action by the Government to pursue its policy of financial inclusion
Solution (b)
Consider the following actions which the Government can take:
- Devaluing the domestic currency.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs.
Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit?
(a.) 1 and 2
(b.) 2 and 3
(c.) 3 only
(d.) 1 and 3
Solution (a)
A rapid increase in the rate of inflation is sometimes attributed to the “base effect”. What is “base effect”?(2011)
(a.) It is the impact of drastic deficiency in supply due to failure of crops
(b.) It is the impact of the surge in demand due to rapid economic growth
(c.) It is the impact of the price levels of previous year on the calculation of inflation rate
(d.)None of the statements (a), (b) and (c) ‘given above is correct in this context
Solution (c)
Why is the offering of “teaser loans” by commercial banks a cause of economic concern?(2011)
- The teaser loans are considered to be an aspect of sub-prime lending and banks may be exposed to the risk of defaulters in future.
- In India, the teaser loans are mostly given to inexperienced entrepreneurs to set up manufacturing or export units.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (c)
In the context of Indian economy, consider the following statements :(2011)
- The growth rate of GDP has steadily increased in the last five years.
- The growth rate in per capita income has steadily increased in the last five years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (b)
In India, which of the following have the highest share in the disbursement of credit to agriculture and allied activities?(2011)
(a.) Commercial Banks
(b.) Cooperative Banks
(c.) Regional Rural Banks
(d.) Microfinance Institutions
Solution (a)
Economic growth is usually coupled with (2011)
(a.) Deflation
(b.) Inflation
(c.) Stagflation
(d.) Hyperinflation
Solution (b)
The lowering of Bank Rate by the Reserve Bank of India leads to (2011)
(a.) More liquidity in the market
(b.) Less liquidity in the market
(c.) No change in the liquidity in the market
(d.) Mobilization of more deposits by commercial banks
Solution (a)
Which one of the following is not a feature of “Value Added Tax”? (2011)
(a.) It is a multi-point destination-based system of taxation
(b.) It is a tax levied on value addition at each stage of transaction in the production-distribution chain
(c.) It is a tax on the final consumption of goods or services and must ultimately be borne by the consumer
(d.) It is basically a subject of the Central Government and the State Governments are only a facilitator for its successful implementation
Solution (c)
A “closed economy” is an economy in which (2011)
(a.) the money supply is fully controlled
(b.) deficit financing takes place
(c.) only exports take place
(d.) neither exports nor imports take place
Solution (d)
Both Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) are related to investment in a country. Which one of the following statements best represents an important difference between the two? (2011)
(a.) FII helps bring better management skills and technology, while FDI only brings in capital
(b.) FII helps in increasing capital availability in general, while FDI only targets specific sectors
(c.) FDI flows only into the secondary market, while FII targets primary market
(d.) FII is considered to be more stable than FDI
Solution (b)
Microfinance is the provision of financial services to people of low-income groups. This includes both the consumers and the self-employed. The service/services rendered under micro-finance is/are: (2011)
- Credit facilities
- Savings facilities
- Insurance facilities
- Fund Transfer facilities
Select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 1 and 4 only
(c.) 2 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (d)
Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a.) 1 only
(b.) 1 and 2 only
(c.) 2 and 3 only
(d.) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Why is the Government of India disinvesting its equity in the Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)? (2011)
- The Government intends to use the revenue earned-from the disinvestment mainly to pay back the external debt.
- The Government no longer intends to retain the management control of the CPSEs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a.) I only
(b.) 2 only
(c.) Both 1 and 2
(d.) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (d)
2012 UPSC Prelims Questions and Solutions
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a bankers’ bank. This would imply which of the following? (2012)
- Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
- The RBI lends funds to the commercial banks in times of need.
- The RBI advises the commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Under which of the following circumstances may ‘capital gains’ arise? (2012)
- When there is an increase in the sales of a product
- When there is a. natural increase in the value of the property owned
- When you purchase a painting and there is a growth in its value due to increase in its popularity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (b)
Which of the following measures would result in an increase in the money supply in the economy? (2012)
- Purchase of government securities from the public by the Central Bank
- Deposit of currency in commercial banks by the public
- Borrowing by the government from the Central Bank
- Sale of government securities to the public by the Central Bank
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Solution (c)
Which of the following would include Foreign Direct Investment in India? (2012)
- Subsidiaries of companies in India
- Majority foreign equity holding in Indian companies
- Companies exclusively financed by foreign companies
- Portfolio investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 only
Solution (d)
Consider the following statements: (2012)
The price of any currency in international market is decided by the
- World Bank
- demand for goods/services provided by the country concerned
- stability of the government of the concerned country
- economic potential of the country in question
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Solution (b)
The basic aim of Lead Bank Scheme is that: (2012)
(a) big banks should try to open offices in each district
(b) there should be stiff competition among the various nationalized banks
(c) individual banks should adopt particular districts for intensive development
(d) all the banks should make intensive efforts to mobilize deposits
Solution (c)
In India, in the overall Index of Industrial Production, the Indices of Eight Core Industries have a combined weight of 37-90%. Which of the following are among those Eight Core Industries? (2012)
- Cement
- Fertilizers
- Natural gas
- Refinery products
- Textiles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
(a) 1 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Solution (c)
The balance of payments of a country is a systematic record of (2012)
(a) all import and transactions of a during a given period normally a year
(b) goods exported from a country during a year
(c) economic transaction between the government of one country to another
(d) capital movements from one country to another
Solution (a)
The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of (2013)
- liquidity of assets
- branch expansion
- merger of banks
- winding-up of banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (d)
An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the: (2013)
(a) market rate of interest is likely to fall
(b) Central Bank is no longer making loans to commercial banks
(c) Central Bank is following an easy money policy
(d) Central Bank is following a tight money policy
Solution (d)
In India, deficit financing is used for raising resources for (2013)
(a) economic development
(b) redemption of public debt
(c) adjusting the balance of payments
(d) reducing the foreign debt
Solution (a)
Which of the following constitute Capital Account? (2013)
- Foreign Loans
- Foreign Direct Investment
- Private Remittances
- Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Solution (b)
Consider the following statements : (2013)
- Inflation benefits the debtors.
- Inflation benefits the bond-holders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (a)
Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Solution (c)
Consider the following liquid assets: (2013)
1.Demand deposits with the banks
2.Time deposits with the banks
3.Savings deposits with the banks
4.Currency
The correct sequence of these decreasing order of Liquidity is
(a) 1-4-3-2
(b) 4-3-2-1
(c) 2-3-1-4
(d) 4-1-3-2
Solution (d)
In the context of Indian economy,Open Market Operations’ refers to: (2013)
(a) borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
(b) lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
(c) purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
(d) None of the above
Solution (c)
Priority Sector Lending by banks in India constitutes the lending to: (2013)
(a) agriculture
(b) micro and small enterprises
(c) weaker sections
(d) All of the above
Solution (d)
A rise in general level of prices may be caused by: (2013)
- an increase in the money supply
- a decrease in the aggregate level of output
- an increase in the effective demand
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (d)
Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves? (2013)
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
(c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
(d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Solution (b)
Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary in its effect? (2013)
(a) Repayment of public debt
(b) Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
(c) Borrowing from banks to finance a budget deficit
(d) Creating new money to finance a budget deficit
Solution (d)
Supply of money remaining the same when there is an increase in demand for money, there will be: (2013)
(a) a fall in the level of prices
(b) an increase in the rate of interest
(c) a decrease in the rate of interest
(d) an increase in the level of income and employment
Solution (b)
Economic growth in country X will necessarily have to occur if (2013)
(a) there is technical progress in the world economy
(b) there is population growth in X
(c) there is capital formation in X
(d) the volume of trade grows in the world economy
Solution (c)
The national income of a country for a given period is equal to the: (2013)
(a) total value of goods and services produced by the nationals
(b) sum of total consumption and investment expenditure
(c) sum of personal income of all individuals
(d) money value of final goods and services produced
Solution (a)
Which of the following grants/ grant direct credit assistance to rural households? (2013)
- Regional Rural Banks
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
- Land Development Banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (c)
The terms ‘Marginal Standing Facility Rate’ and ‘Net Demand and Time Liabilities’, sometimes appearing in news, are used in relation to (2014)
- banking operations
- communication networking
- military strategies
- supply and demand of agricultural products
Solution (a)
What is/are the facility/facilities the beneficiaries can get from the services of Business Correspondent (Bank Saathi) in branchless areas?(2014)
- It enables the beneficiaries to draw their subsidies and social security benefits in their villages.
- It enables the beneficiaries in the rural areas to make deposits and withdrawals.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Solution (c)
If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (2014)
- decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
- increase the tax collection of the Government
- increase the investment expenditure in the economy
- increase the total savings in the economy
Solution (3)
In the context of Indian economy which of the following is/are the purpose/purposes of ‘Statutory Reserve Requirements’?
- To enable the Central Bank to control the amount of advances the banks can create
- To make the people’s deposits with banks safe and liquid
- To prevent the commercial banks from making excessive profits
- To force the banks to have sufficient vault cash to meet their day-to-day requirements
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (b)
If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will
- decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
- increase the tax collection of the Government
- increase the investment expenditure in the economy
- increase the total savings in the economy
Solution (c)
With reference to Union Budget, which of the following is/are covered under Non-Plan Expenditure?
- Defense -expenditure
- Interest payments
- Salaries and pensions
- Subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- None
Solution (c)
The sales tax you pay while purchasing a toothpaste is a
- tax imposed by the Central Government.
- tax imposed by the Central Government but collected by the State Government
- tax imposed by the State Government but collected by the Central Government
- tax imposed and collected by the State Government
Solution (d)
The main objective of the 12th Five-Year Plan is
- inclusive growth and poverty reductions
- inclusive and sustainable growth
- sustainable and inclusive growth to reduce unemployment
- Faster, sustainable and more inclusive growth.
Solution (d)
What does venture capital mean?
- A short-term capital provided to industries
- A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
- Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
- Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Solution (b)
With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account?
- Balance of trade
- Foreign assets
- Balance of invisibles
- Special Drawing Right
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 4
Solution (c)
Which of the following organizations brings out the publication known as ‘World Economic Outlook’?
- The International Monetary Fund
- The United Nations Development Programme
- The World Economic Forum
- The World Bank
Solution (a)
Demographics:
India is regarded as a country with “Demographic Dividend”. This is due to: (2011)
(a.) Its high population in the age group below 15 years
(b.) Its high population in the age group of 15-64 years
(c.) Its high population in the age group above 65 years
(d.) Its high total population
Solution (b)
Consider the following specific stages of demographic transition associated with economic development : (2012)
- Low birthrate with low death rate
- High birthrate with high death rate
- High birthrate with low death rate
Select the correct order of the above stages using the codes given below :
(a) 1, 2, 3
(b) 2, 1, 3
(c) 2, 3, 1
(d) 3, 2, 1
Solution (c)
To obtain full benefits of demographic dividend, what should India do? (2013)
(a) Promoting skill development
(b) Introducing more social security schemes
(c) Reducing infant mortality rate
(d) Privatization of higher education
Solution (a)on (a)
No comments:
Post a Comment